OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effect of equalizing and nonequalizing resistance training volume on pain intensity, disability, and strength in individuals with patellofemoral pain (PFP). DESIGN: Intervention systematic review with meta-analysis. LITERATURE SEARCH: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, CINAHL, Physiotherapy Evidence Database, Scopus, SPORTDiscus, and Epistemonikos were searched from inception to December 2024. STUDY SELECTION CRITERIA: Randomized controlled trials that assessed the effects of any resistance exercise in individuals with PFP were included. The studies were categorized into groups with equalized and nonequalized total training volumes. DATA SYNTHESIS: Separate random-effects meta-analyses comparing equalizing (experimental versus control) and nonequalizing (higher versus lower) resistance training volume were conducted. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2, and certainty of evidence was judged according to the GRADE framework. RESULTS: Thirty-seven randomized controlled trials (1853 participants) were included. The higher training volume group had improved pain intensity immediately after the intervention (SMD, -0.88; 95% CI: -1.39, -0.36) and beyond the intervention period (MD, -1.66; 95% CI: -3.02, -0.31), and improved disability immediately after the intervention (SMD, 0.66; 95% CI: 0.19, 1.12) and beyond the intervention period (SMD, 1.03; 95% CI: 0.22, 1.84) compared to the lower training volume group. When the training volume was equalized, there were no differences between the groups. There was no difference in muscle strength between the groups in equalized and nonequalized volumes. CONCLUSION: There was very low-certainty evidence that higher resistance training volume yielded better outcomes for pain intensity and disability compared to a lower volume. Equalized training volumes showed no differences. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2025;55(6):1-12. Epub 8 May 2025. doi:10.2519/jospt.2025.13062.
| Discipline Area | Score |
|---|---|
| Rehab Clinician (OT/PT) | 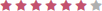 |





 , McMaster University
, McMaster University