PURPOSE: Acupuncture shows potential as a treatment for sciatica, but the credibility and consistency of supporting evidence remain unclear, warranting critical and comprehensive evaluation. This overview is aims to assess the reliability, adequacy, and limitations of current evidence on acupuncture for sciatica using a multidimensional approach and further examine its efficacy through a secondary meta-analysis.
METHODS: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses (SRs/MAs) meeting PICOS criteria were identified from eight databases by two independent reviewers. Evidence reliability was assessed using AMSTAR-2, ROBIS, PRISMA-A, and the GROOVE tool across four domains: methodological quality, bias risk, reporting accuracy, and study overlap. Duplicate randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were excluded based on the Corrected Covered Area (CCA) analysis, and a secondary meta-analysis was conducted. Sensitivity analyses and funnel plots assessed robustness and publication bias.
RESULTS: Seven SRs/MAs were included. AMSTAR-2 revealed significant methodological flaws, particularly due to a lack of protocol pre-registration. ROBIS assessments showed a high risk of bias, with most studies relying on single-database searches and lacking comprehensive strategies. PRISMA-A indicated generally low reporting quality, especially regarding descriptions of acupuncture sensation. The GROOVE tool yielded a CCA of 7.23%, reflecting moderate study overlap. The secondary meta-analysis showed that acupuncture significantly improved treatment effectiveness (RR = 1.23; 95% CI: 1.20-1.26; P = 0.008), reduced pain intensity, and increased pain threshold. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of results, while funnel plots suggested some publication bias. Acupuncture was generally considered safe across studies.
CONCLUSION: Although current evidence is limited by methodological flaws, publication bias, and poor reporting quality, acupuncture shows promising clinical potential for sciatica. High-quality, rigorously designed studies are needed to confirm its efficacy.
| Discipline Area | Score |
|---|---|
| Rehab Clinician (OT/PT) | 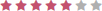 |
| Physician |  |





 , McMaster University
, McMaster University