OBJECTIVE: To compare the effect of combining proprioceptive exercises with strengthening exercises versus strengthening exercises alone, on shoulder pain and disability in individuals with chronic rotator cuff-related shoulder pain (RCRSP). DESIGN: Parallel group randomized controlled trial. METHODS: Seventy individuals with chronic RCRSP were randomly assigned to either the control group (n = 35; muscle strengthening exercises) or the experimental group (n = 35; muscle strengthening combined with proprioceptive exercises) for a 2-month program of supervised and home-based exercises. The primary outcome, the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI), was assessed at baseline, 2 months, and 5 months, while the secondary outcomes (pain intensity, proprioception, isokinetic muscle strength, catastrophizing, kinesiophobia, and self-efficacy), were evaluated at baseline and 2 months. A linear mixed model was used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: There was no significant group-by-time interaction for the SPADI (P = .25). Significant time effects, but no between-group differences, were found for improvements in pain intensity, kinesiophobia, catastrophizing, self-efficacy, kinesthesia, and joint position sense, while a decline in lateral rotator peak torque was noted. CONCLUSION: Combining proprioceptive with shoulder strengthening exercises did not lead to additional improvements across all outcomes in individuals with chronic RCRSP. The lack of a nonintervention group limits the ability to determine whether the improvements in both groups were due to the exercise programs or to natural recovery. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2025;55(7):495-511. Epub 16 June 2025. doi:10.2519/jospt.2025.13097.
| Discipline Area | Score |
|---|---|
| Physician | 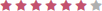 |
| Rehab Clinician (OT/PT) | 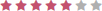 |
Rehab Clinician (OT/PT) rater
A detailed study that is well written. It is useful to know that adding additional proprioception exercises does not improve chronic rotator cuff pain and function. It means that we do not need to divide our time and can focus on strengthening exercises. There was some additional improvement in the proprioception group that did not reach the level of significance for this study but is an avenue for further research. The proprioception group may have improved more over time outside of the follow-up time of the study. There may still be some benefit of incorporating some proprioception exercises. At the very least they might add some variety and interest into the clinical options. Some strengthening might still occur, and some patients might be more compliant with a set of exercises that they perceive as more interesting.
Rehab Clinician (OT/PT) rater
The trial is likely underpowered.





 , McMaster University
, McMaster University